TLA+的入门,原理
TLA+简介
[TOC]
1. 几个问题(Why)
问题样例
例子1
---- MODULE transfer_money ----
EXTENDS Naturals, TLC
(* --algorithm transfer {
variables
alice_account = 10,
bob_account = 10,
account_total = alice_account + bob_account;
process(transaction \in 1..2)
variable money \in 1..20;
{
start:
if (alice_account >= money)
{
A:
alice_account := alice_account - money;
bob_account := bob_account + money;
};
}
}*)
MoneyNotNegative == money >= 0
MoneyInvariant == alice_account + bob_account = account_total
====
例子2
DieHard 虎胆龙威。 两个水壶,一个3升容量,一个5升,怎么得到4升水?
TLA+的检查结果
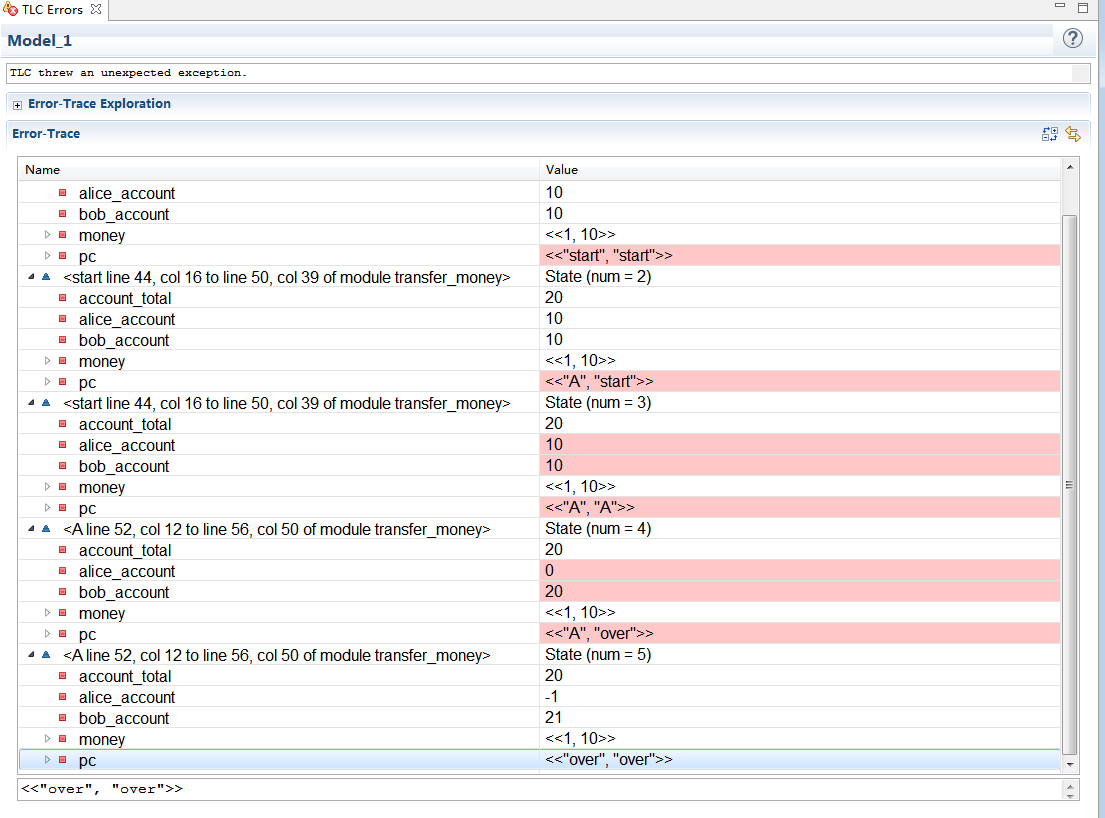
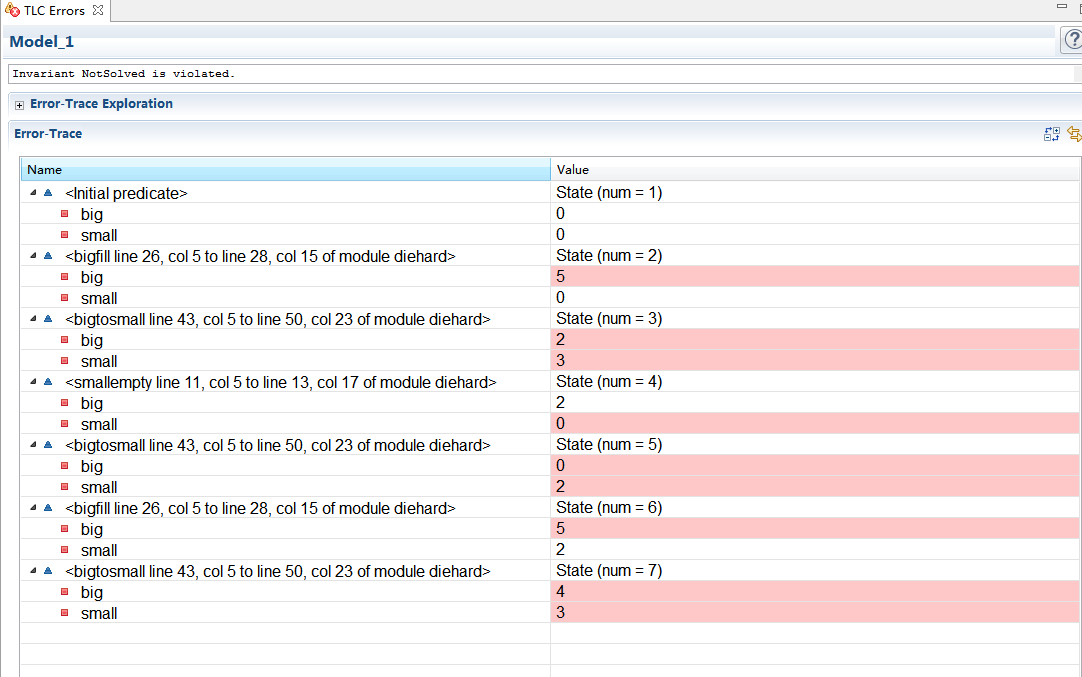
3. TLA+是什么(What)
定义
Temporal logic of actions (TLA) TLA+ is a high-level language for modeling programs and systems–especially concurrent and distributed ones. It’s based on the idea that the best way to describe things precisely is with simple mathematics. TLA+ and its tools are useful for eliminating fundamental design errors, which are hard to find and expensive to correct in code.
用数学来精确建模。
历史
temporal logic 在1957年就提出来了,lamport认为其是abstract nonsence抽象的废话,没有实际应用,实际上是行不通的。 但他认为很有趣,所以继续研究。 后面lamport继续研究可行的实践方法practical method of specification, 1983年”Specifying Concurrent Programming Modules”论文,提出the idea of describing state transitions as boolean-valued functions of primed and unprimed variables. 引入了将状态转换描述为primed变量和unprimed变量的布尔值函数的想法。 1990年temporal logic of actions论文, 1994年正式发布 “The Temporal Logic of Actions” ,TLA enabled the use of actions in temporal formulas,是一个优雅的方法。 TLA specifications mostly consisted of ordinary non-temporal mathematics, which Lamport found less cumbersome than a purely temporal specification. TLA规范主要由普通的非时间性数学组成,Lamport发现它们比纯时间性规范少了很多麻烦。
Temporal logic of actions (TLA) is a logic developed by Leslie Lamport, which combines temporal logic with a logic of actions. It is used to describe behaviours of concurrent systems. 重点就是在temporal formulas中引入了action。
在微软,亚马逊有很多TLA+应用,且评价很高。
理论
抽象定义
去掉非关键部分和实现细节,对关键部分建立模型。
对Disital systems的抽象
Disital systems的连续执行可以被描述为一些离散step的sequence。如时钟的抽象。 TLA用一个state change描述step。 系统的执行,就被描述为step的sequence。 通过随time改变的state来对系统建模。
state:TLA用对variable的赋值来描述state。把各种可能性做乘法得到大量的state。 behaver(状态序列): state之间的转换轨迹。 state的一个sequeence。 所以系统的一个执行路径:就被描述为一个behavior。 我们想描述 一个系统的所有执行, 即想描述一个系统的所有可能behavior。
state machine
我们可以用state machine来抽象他们。 state machine可以通过如下来描述:
- all possible inital states
- what next states can follow any given state
It halts if there is no possible next state
用state machine描述的步骤:
- what the variables are
- possible initial values of variables
- a relation between their values in the current state and their possible values in the next state 变量在当前状态下的值 与 下一个状态下值之间的关系
例子
int i; <-- init state
void main()
{
i = someNumber(); <-- start state
i = i+1; <-- middle state
}
用数学formula来描述state machine:
- 这个数学表示,不是描述计算的执行指令(即下一步应该do什么),而是formula。It means : if pc = “start” the formula equals the THEN formula, otherwise it equals the ELSE formula. 而不是if pc=’start’, do the THEN part.
- formula的值只有true和false
- Next-state formula describes all permitted steps。
next-state formula == IF pc = "start" THEN (i' \in 0..1000) /\ (pc = "middle") ELSE IF pc = "middle" THEN (i' = i+1) /\ (pc' = "done") ELSE FALSE另一种更好的写法:
next-state formula == \/ /\ pc = "start" /\ i' \in 0..1000 /\ pc' = "middle" \/ /\ pc = "middle" /\ i' = i + 1 /\ pc' = "done"
基本概念
TLA+ uses several terms which require definition:
- State - an assignment of values to variables 值到变量的“赋值”
- Behaviour - a sequence of states
- Step - a pair of successive states in a behavior behavior内连续的两个state
- Stuttering step - a step during which variables are unchanged 变量未变的step
- Next-state relation - a relation describing how variables can change in any step 描述在step内变量怎么变化的关系(p’=p+1)
- State function - an expression containing variables and constants that is not a next-state relation 没看懂
- State predicate - a Boolean-valued state function
- Invariant - a state predicate true in all reachable states
- Temporal formula - an expression containing statements in temporal logic. 比如Spec就是一个。
-
Properties - A property is a predicate on behaviors—that is, it assigns a boolean value (true or false) to every behavior. In TLA+, properties are written as temporal formulas.
- non-primed variables - The meaning of the non-primed variables is the variable’s value in this state.
- primed variables - The meaning of primed variables is the variable’s value in the next state.
-
action - An action is an expression containing primed and non-primed variables, such as x + x’ * y = y’. The above expression means the value of x today, plus the value of x tomorrow times the value of y today, equals the value of y tomorrow.
- [Action]{variables} Statements in temporal logic are of the form [A]{t}, where A is an action and t contains a subset of the variables appearing in A. The meaning of [A]_{t} is that either A is valid now, or the variables appearing in t do not change. This allows for stuttering steps, in which none of the program variables change their values.
TLA+的原理
原理
State就是给变量的赋值(应该就是指某个具体的值) Init 是初始state Next-state relation: (也叫next-state action)描述变量在一个step内是怎么变化的。是一个返回bool值的formula。描述的是step。有些是永远返回true的
运作机制
- 给定Init state 和 Next-state action。 两个都是formula方程式
- 利用计算机的算力,从init开始暴力解next formula(结果是true的)来搜索下一个state(横向遍历init及Next)
- 循环往复,最终得到所有sequence of state。
- 在该过程中,TLC可以检查是否有next formula失败(返回FALSE),或者检查invariant失败。即是否满足约束条件。
能干啥?
要靠大家探索!
- 逻辑是否完整
- 约束是否满足(deadlock,Termination)
功能
TLA+是基于一阶逻辑(与或非,推导,等价)和集合的基本数学理论的,语言表现性强大,很容易描述复杂的情况。
主要两个功能:
- 通过TLA+或plusCal语言描述建模,
- 通过TLC工具检查。
语言的描述功能是无限的,TLC的检查功能是有限的,只能检查一个子集。
TLC Model checker
TLC只能检查TLA+的一部分,要求是finite state and enumerable。 TLC在所有定义的state transtions上进行搜索,当所有state transtion都产生已经发现的state时才停止。 当TLC发现一个state违背了invariant时就报错。
The TLC model checker builds a finite state model of TLA+ specifications for checking invariance properties. TLC generates a set of initial states satisfying the spec, then performs a breadth-first search over all defined state transitions. Execution stops when all state transitions lead to states which have already been discovered. If TLC discovers a state which violates a system invariant, it halts and provides a state trace path to the offending state. TLC provides a method of declaring model symmetries to defend against combinatorial explosion.[14] It also parallelizes the state exploration step, and can run in distributed mode to spread the workload across a large number of computers.[20]
As an alternative to exhaustive breadth-first search, TLC can use depth-first search or generate random behaviours. TLC operates on a subset of TLA+; the model must be finite and enumerable, and some temporal operators are not supported. In distributed mode TLC cannot check liveness properties, nor check random or depth-first behaviours. TLC is available as a command line tool or bundled with the TLA toolbox.
4.语言语法
参见”语言框架”,”plusCal语法” 文档。
5. TLA+ toolbox的使用
使用方法。
6. 进一步的学习
We witnessed first hand the brain washing done by years of C programming.
链接及内容
- 主页
- 理论Introduction to TLA+ 作者录得video,一定看看
- 理论State Machines in TLA+ 作者录得video,一定看看
- 实践入门,从helloworld开始,层层加码
- plusCal语法
- specifying system 里面有讲解TLA+语法,TLC运作机制,怎么描述系统。
- [wiki 引用1] (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TLA%2B)
- [wiki 引用2] (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Temporal_logic_of_actions)